W2E SOLUTION THAT WORKS |
| |
 |
The W2E solution utilizes a simple approach, using the client's
current infrastructure to provide hydrogen for local consumption.
The W2E solution consists of the following elements:
• W2E will utilize locally generated wastes to produce hydrogen,
instead of expensive fuels.
• Hydrogen is produced for local consumption; therefore it is not
dependent upon a distribution infrastructure or external market.
• Hydrogen is produced from wastes with the generation of
synfuels as an intermediary step. In the event that the hydrogen
demand is diminished, the synfuels can be used to replace any
other fuels used locally to produce heat, power or steam.
• W2E will utilize versatile, small-scale, waste-to-hydrogen
systems that will operate with various types of wastes, including municipal wastes, industrial wastes, food wastes,
biomass, animal wastes, agricultural wastes, municipal sludge,
and any other waste that has a carbon content.
• W2E’s solution for waste-to-hydrogen will be equally effective
for conventional fuels for producing hydrogen and therefore
this solution would have a backup when wastes are not
available.
|
|
| |
| W2E Technology |
| |
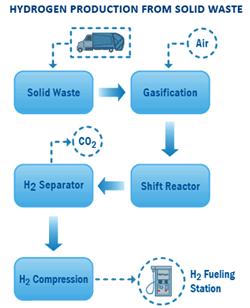
W2E utilizes a small-scale waste gasification system for converting
wastes to hydrogen. This includes the conversion of organic containing
solid, liquid and gaseous wastes into uniform and clean
burning synthesis gas as an intermediate step with its ultimate
conversion to hydrogen as a final step. The process converts any
solid, liquid, and gaseous organic wastes that have a fuel value;
using air and water to create reactions, which in turn, produce
uniform synthesis gas. This W2E solution is very flexible and can
be applied to varied, locally generated wastes, such as forestry
and agricultural residues, animal wastes, bacterial sludge, sewage
sludge, municipal solid waste, food wastes, animal bovine parts,
fungal material, industrial solid waste, waste tires, coal washing
residue, petroleum coke, oil shale, even coal, peat and lignite,
waste oil, industrial liquid wastes, residuals from petroleum
refining and volatile organic compounds generated by the
industrial processes. The W2E solution converts these wastes into
gaseous fuels with the maximum conversion efficiency available in
a gasification technology.
During the gasification of wastes, the majority of solid wastes
break down into simple gases. The transformation of solid wastes
into gaseous fuel is carried out in substoichiometric conditions.
In this process, the air supply to the reactor is kept below that
required for complete combustion, generating fuel gas from the
solid wastes, which consists primarily of a mixture of hydrogen,
carbon monoxide, carbon dioxide, methane and water vapor, while
the solid residue is comprised primarily of ash. After cleaning, this
fuel gas can be used directly for producing electricity, steam, or
combined heat and power.
For hydrogen production, this mixture of gases is further reacted
with more steam to convert carbon monoxide into hydrogen and
carbon dioxide. The hydrogen is then separated from the gas
mixture by using a pressure swing adsorption (PSA) process to yield
99.999% pure hydrogen. |
| |
HYDROGEN PRODUCTION POTENTIAL FROM WASTES |
|
As a practical note, each person in the United States on an average
generates about 4.5 pounds of waste per day, or over 1600
pounds per year, most of which is deposited in municipal solid
waste (MSW) landfills. For a town with a population of 10,000
inhabitants, the average daily production of wastes is in the range
of 45,000 pounds per day, or approximately 1 ton per hour. This
is a significant quantity. When this is added to the other wastes
that are generated by nearby industries, including waste oils, waste tires, packaging materials, used gloves, and others, we are looking
at least 2 tons per hour of an excellent resource for hydrogen.
The wastes can be treated individually or as mixtures. Based on
above numbers one can safely assume that 1 t/h or 24 t/d of
mixed waste will easily generate over 2000 kg/d of hydrogen which
is enough to service a fleet of 400 vehicles.
|
| |
|
| |
|
|
 |
Wastes are a Domestic Resource......that can be used to produce energy in sustainable reliable and economical way. |

|
| |
|
|

